Anaplasmosis is a sickness caused by a rickettsial parasite of ruminants, Anaplasma spp. The microorganism is gram-negative,[1] and taints red blood cells.[2] It is transmitted by characteristic means through various haematophagous types of ticks. Anaplasmosis can likewise be transmitted by the utilization of surgical, dehorning, mutilation, and tattoo instruments and hypodermic needles that are not sterilized between employments.
Signs and side effects
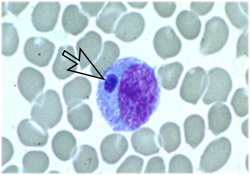
Pallor might be extreme and result in cardiovascular changes, for example, an expansion in heart rate. Blood in the pee may happen because of the lysis of red platelets. General fundamental signs, for example, loose bowels, anorexia and weight reduction may likewise be available. A blood spread recolored with Giemsa ought to be watched for distinguishing proof of tainted red platelets and will permit complete diagnosis.[4]
Aversion
Antibodies against anaplasmosis are accessible. Transporter creatures ought to be disposed of from herds. Tick control may likewise be helpful in spite of the fact that it can be hard to implement.[4]
Treatment
Treatment more often than not includes a solution of doxycycline (a typical dosage would be 100 mg at regular intervals for grown-ups) or a comparable class of anti-microbials. Oxytetracycline and imidocarb have additionally been appeared to be compelling. Steady treatment, for example, blood items and liquids might be necessary.[4]
In the United States, anaplasmosis is quite present in the south and west where the tick has Ixodes spp. are found. It is additionally an apparently expanding counter acting agent in people in Europe.[1] Although antibodies have been produced, none are as of now accessible in the United States. Right on time in the twentieth century, this sickness was viewed as one of major monetary outcome in the western United States. In the 1990s, control of ticks through new acaricides and handy treatment with delayed activity anti-infection agents, outstandingly antibiotic medication, has prompted the point where the illness is never again thought about a noteworthy issue.
In 2005, Anaplasma ovis was found in reindeer populaces in Mongolia.[5] This pathogen and its related disorder (portrayed by dormancy, fever and pale mucous films) was already just saw in wild sheep and goats in the locale, and is the principal watched occasion of A. ovis in reindeer.
In Australia, cow-like anaplasmosis, caused by Anaplasma marginale, is just found in the northern and eastern parts of Australia where the dairy cattle tick is available. It was likely presented as ahead of schedule as 1829 by cows from Indonesia plagued with the cows tick Boophilus microplus.[6]
The veterinarian George P. Broussard of New Iberia, Louisiana, directed essential research anaplasmosis and brucellosis.[7]
No comments:
Post a Comment