Stroke is a restorative condition in which poor blood stream to the cerebrum brings about cell death.[4] There are two principle sorts of stroke: ischemic, because of absence of blood stream, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding.[4] They result in part of the mind not working properly.[4] Signs and side effects of a stroke may incorporate a failure to move or feel on one side of the body, issues understanding or talking, feeling like the world is turning, or loss of vision to one side.[1][2] Signs and side effects frequently show up not long after the stroke has occurred.[2] If manifestations last short of what maybe a couple hours it is known as a transient ischemic assault (TIA) or smaller than normal stroke.[2] A hemorrhagic stroke may likewise be related with a serious headache.[2] The indications of a stroke can be permanent.[4] Long-term complexities may incorporate pneumonia or loss of bladder control.[2]
The primary hazard factor for stroke is high blood pressure.[5] Other hazard factors incorporate tobacco smoking, heftiness, high blood cholesterol, diabetes mellitus, past TIA, and atrial fibrillation.[1][5] An ischemic stroke is normally caused by blockage of a vein, however there are additionally less regular causes.[9][10][11] A hemorrhagic stroke is caused by either draining specifically into the cerebrum or into the space between the mind's membranes.[9][12] Bleeding may happen due to a cracked mind aneurysm.[9] Diagnosis is ordinarily with restorative imaging, for example, a CT check or attractive reverberation imaging (MRI) examine alongside a physical exam.[6] Other tests, for example, an electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood tests are done to decide chance factors and preclude other conceivable causes.[6] Low glucose may cause comparable symptoms.[6]
Aversion incorporates diminishing danger factors, and additionally potentially ibuprofen, statins, surgery to open up the conduits to the mind in those with tricky narrowing, and warfarin in those with atrial fibrillation.[1] A stroke or TIA regularly requires crisis care.[4] An ischemic stroke, if recognized inside three to four and half hours, might be treatable with a drug that can separate the clot.[1] Aspirin ought to be used.[1] Some hemorrhagic strokes advantage from surgery.[1] Treatment to endeavor to recuperate lost capacity is called stroke restoration and in a perfect world happens in a stroke unit; in any case, these are not accessible in a great part of the world.[1]
In 2013 roughly 6.9 million individuals had an ischemic stroke and 3.4 million individuals had a hemorrhagic stroke.[13] In 2015 there were around 42.4 million individuals who had beforehand had a stroke were still alive.[7] Between 1990 and 2010 the quantity of strokes which happened every year diminished by around 10% in the created world and expanded by 10% in the creating world.[14] In 2015, stroke was the second most continuous reason for death after coronary supply route infection, representing 6.3 million passings (11% of the total).[8] About 3.0 million passings came about because of ischemic stroke while 3.3 million passings came about because of hemorrhagic stroke.[8] About portion of individuals who have had a stroke live short of what one year.[1] Overall, 66% of strokes happened in those more than 65 years old.[14]
Characterization
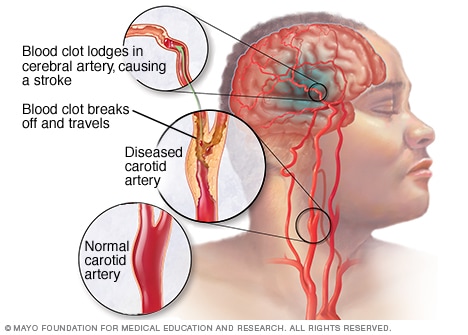
Strokes can be characterized into two noteworthy classes: ischemic and hemorrhagic.[15] Ischemic strokes are caused by interference of the blood supply to the cerebrum, while hemorrhagic strokes result from the break of a vein or a strange vascular structure. Around 87% of strokes are ischemic, the rest being hemorrhagic. Draining can create inside territories of ischemia, a condition known as "hemorrhagic change." It is obscure what number of hemorrhagic strokes really begin as ischemic strokes.[1]
Definition
In the 1970s the World Health Organization characterized stroke as a "neurological shortage of cerebrovascular reason that perseveres past 24 hours or is hindered by death inside 24 hours",[16] in spite of the fact that "stroke" is hundreds of years old. This definition should mirror the reversibility of tissue harm and was conceived for the reason, with the time span of 24 hours being picked discretionarily. The 24-hour restrain partitions stroke from transient ischemic assault, which is a related disorder of stroke indications that determination totally inside 24 hours.[1] With the accessibility of medicines which can diminish stroke seriousness when given early, numerous now lean toward elective phrasing, for example, cerebrum assault and intense ischemic cerebrovascular disorder (displayed after heart assault and intense coronary disorder, separately), to mirror the desperation of stroke side effects and the need to act swiftly.[17]
Ischemic
Primary articles: Cerebral localized necrosis and Brain ischemia
In an ischemic stroke, blood supply to some portion of the mind is diminished, prompting brokenness of the cerebrum tissue here. There are four reasons why this may happen:
Thrombosis (check of a vein by a blood coagulation framing locally)
Embolism (check because of an embolus from somewhere else in the body, see below),[1]
Foundational hypoperfusion (general diminishing in blood supply, e.g., in shock)[18]
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.[19]
Stroke without a conspicuous clarification is named "cryptogenic" (of obscure birthplace); this constitutes 30-40% of all ischemic strokes.[1][20]
There are different order frameworks for intense ischemic stroke. The Oxford Community Stroke Project grouping (OCSP, otherwise called the Bamford or Oxford characterization) depends basically on the underlying manifestations; in light of the degree of the indications, the stroke scene is named add up to front course infarct (TACI), fractional foremost dissemination infarct (PACI), lacunar infarct (LACI) or back flow infarct (POCI). These four elements anticipate the degree of the stroke, the territory of the cerebrum that is influenced, the hidden reason, and the prognosis.[21][22] The TOAST (Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment) characterization depends on clinical side effects and in addition consequences of further examinations; on this premise, a stroke is delegated being because of (1) thrombosis or embolism because of atherosclerosis of a vast corridor, (2) an embolism starting in the heart, (3) finish blockage of a little vein, (4) other decided reason, (5) undetermined reason (two conceivable causes, no reason recognized, or fragmented investigation).[23] Users of stimulants, for example, cocaine and methamphetamine are at a high hazard for ischemic strokes.[24]
Hemorrhagic
Fundamental articles: Intracerebral discharge and Subarachnoid drain
CT sweep of an intraparenchymal drain (base bolt) with encompassing edema (top bolt)
There are two fundamental sorts of hemorrhagic stroke:[25][26]
Intracerebral drain, which is essentially seeping inside the mind itself (when a vein in the cerebrum blasts, flooding the encompassing tissue with blood), due to either intraparenchymal discharge (seeping inside the mind tissue) or intraventricular drain (seeping inside the cerebrum's ventricular framework).
Subarachnoid discharge, which is fundamentally draining that happens outside of the cerebrum tissue yet at the same time inside the skull, and correctly between the arachnoid mater and pia mater (the sensitive deepest layer of the three layers of the meninges that encompass the mind).
The over two primary kinds of hemorrhagic stroke are likewise two unique types of intracranial drain, which is the aggregation of blood anyplace inside the cranial vault; yet alternate types of intracranial discharge, for example, epidural hematoma (seeping between the skull and the dura mater, which is the thick furthest layer of the meninges that encompass the mind) and subdural hematoma (seeping in the subdural space), are not viewed as "hemorrhagic strokes".[27]
Hemorrhagic strokes may happen on the foundation of changes to the veins in the mind, for example, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, cerebral arteriovenous deformity and an intracranial aneurysm, which can cause intraparenchymal or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
No comments:
Post a Comment